Mapping Iran: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Diverse Geography
**Table of Contents** * [Unveiling Iran's Geographic Canvas](#unveiling-irans-geographic-canvas) * [Area and Global Standing](#area-and-global-standing) * [Strategic Crossroads: A Geopolitical Hub](#strategic-crossroads-a-geopolitical-hub) * [Defining Iran's Borders and Coastal Majesty](#defining-irans-borders-and-coastal-majesty) * [Land Boundaries: Neighbors and Distances](#land-boundaries-neighbors-and-distances) * [Maritime Frontiers: Seas and Gulfs](#maritime-frontiers-seas-and-gulfs) * [The Spine of the Land: Iran's Mountain Ranges](#the-spine-of-the-land-irans-mountain-ranges) * [The Majestic Elburz: Guardian of the North](#the-majestic-elburz-guardian-of-the-north) * [The Central Kuh Rud and Western Zagros](#the-central-kuh-rud-and-western-zagros) * [Iran's Arid Heart: The Great Deserts](#irans-arid-heart-the-great-deserts) * [Dasht-e Kavir: The Great Salt Desert](#dasht-e-kavir-the-great-salt-desert) * [Dasht-e-Lut: A Land of Extremes](#dasht-e-lut-a-land-of-extremes) * [Climate, Seismic Activity, and Natural Heritage](#climate-seismic-activity-and-natural-heritage) * [A Tapestry of Climates](#a-tapestry-of-climates) * [Living on Active Fault Lines: Seismic Iran](#living-on-active-fault-lines-seismic-iran) * [Flora and Fauna: Iran's Natural Treasures](#flora-and-fauna-irans-natural-treasures) * [From Ancient Empires to Modern Provinces: A Historical Geographic Perspective](#from-ancient-empires-to-modern-provinces-a-historical-geographic-perspective) * [Mapping History: Persia (Iran), Afghanistan and Baluchistan (1897 Map)](#mapping-history-persia-iran-afghanistan-and-baluchistan-1897-map) * [Iran's Administrative Divisions: Provinces and Major Cities](#irans-administrative-divisions-provinces-and-major-cities) * [Economic Geography: Resources and Energy](#economic-geography-resources-and-energy) * [Underground Riches: Oil and Gas](#underground-riches-oil-and-gas) * [Beyond Hydrocarbons: Other Natural Resources](#beyond-hydrocarbons-other-natural-resources) * [Exploring Iran: Travel and Cultural Geography](#exploring-iran-travel-and-cultural-geography) * [Iconic Destinations and Geographic Wonders](#iconic-destinations-and-geographic-wonders) * [Understanding Iran: Key Facts and FAQs](#understanding-iran-key-facts-and-faqs)
--- ### Unveiling Iran's Geographic Canvas To truly appreciate the "iran geography map," one must first grasp its sheer scale and strategic positioning. Iran occupies a vast area in Southwestern Asia, characterized by a mix of rugged mountains, expansive deserts, and fertile plains. This diverse terrain has profoundly influenced its historical development, cultural identity, and modern geopolitical role. #### Area and Global Standing Iran covers an impressive area of 1,648,195 square kilometers (636,372 sq mi). To put this into perspective, this makes Iran the 17th largest country in the world by area, though some sources list it as the 18th. Its landmass is roughly equivalent to the combined areas of the United Kingdom, France, Spain, and Germany, or slightly less than the state of Alaska. While smaller than Libya, it is notably larger than Egypt. This vastness contributes to its varied climates and landscapes, making the "iran geography map" a mosaic of different ecological zones. #### Strategic Crossroads: A Geopolitical Hub Iran's central location in Eurasia places it at a critical nexus. It lies at the crossroads between Central and South Asia, the Arab states, and the broader Middle East. This strategic positioning has historically made Iran a significant imperial power and a crucial factor in superpower rivalries. Its control over vital trade routes and proximity to energy resources has cemented its geostrategic importance. Understanding this fundamental aspect of its location is key to comprehending the broader implications of the "iran geography map." ### Defining Iran's Borders and Coastal Majesty The boundaries of Iran are as diverse as its internal landscape, defined by a mix of land borders with seven neighboring countries and extensive coastlines along major bodies of water. These geographical demarcations have played a significant role in shaping Iran's interactions with its neighbors and its global trade. #### Land Boundaries: Neighbors and Distances Iran shares extensive land borders with several nations, each presenting unique historical and contemporary dynamics. To the north, it borders Armenia (35 km / 22 mi), Azerbaijan (432 km / 268 mi, across two separate borders), and Turkmenistan (992 km / 616 mi). To the east, its neighbors are Afghanistan (936 km / 582 mi) and Pakistan (909 km / 565 mi). To the west, Iran shares borders with Iraq (1,458 km / 906 mi) and Turkey (499 km / 310 mi). These extensive land connections highlight Iran's role as a regional bridge and its complex network of relationships, all visible on a detailed "iran geography map." #### Maritime Frontiers: Seas and Gulfs While its land borders are crucial, Iran's maritime frontiers are equally vital, particularly for trade and energy exports. The Caspian Sea defines Iran's northern boundary, providing access to Central Asian markets and Russia. To the south, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman mark its southern limits, with the Strait of Hormuz, a critical choke point for global oil shipments, connecting the two. The Arabian Sea also touches its southeastern coast. These extensive coastlines, prominently featured on any "iran geography map," are vital for Iran's economy and its strategic naval presence. ### The Spine of the Land: Iran's Mountain Ranges The dominant feature of Iran's physical geography is its rugged, mountainous terrain. Indeed, Iran is almost exclusively mountainous along its rim, with a mix of deserts and plains along the coastal areas. These formidable mountain chains have historically provided natural defenses, influenced climate patterns, and dictated population distribution. #### The Majestic Elburz: Guardian of the North The Elburz Mountains lie in the north of Iran, running parallel to the Caspian Sea. This range is home to Mount Damavand, Iran's highest peak and a dormant volcano, soaring to 5,610 meters (18,406 feet). The Elburz range acts as a significant climatic barrier, trapping moisture from the Caspian Sea on its northern slopes, leading to lush, forested areas, while its southern slopes are much drier, transitioning into the central Iranian plateau. This dramatic contrast is a key feature of the "iran geography map." #### The Central Kuh Rud and Western Zagros Spanning the interior of the country are the Kuh Rud Mountains, forming a central spine that separates the two major deserts. To the west, the extensive Zagros Mountains stretch from the border with Turkey and Iraq down to the Persian Gulf. This vast range is characterized by parallel folds and valleys, making it a challenging but historically significant region. The Zagros Mountains are rich in natural resources and have been home to various ethnic groups for millennia. Together, these three major mountain chains—Elburz, Kuh Rud, and Zagros—define the physical character of the "iran geography map," influencing everything from climate to human settlement patterns. ### Iran's Arid Heart: The Great Deserts Despite its mountainous character, a significant portion of Iran's interior is dominated by vast, arid deserts. These desolate yet beautiful landscapes are a defining feature of the "iran geography map," showcasing the country's extreme climatic variations and unique geological formations. #### Dasht-e Kavir: The Great Salt Desert First, the Dasht-e Kavir, or the Great Salt Desert, is located in the central region of Iran. This vast desert is characterized by salt marshes, salt lakes, and dry riverbeds. Its extreme aridity and high temperatures make it one of the most inhospitable places on Earth. The Kavir Desert's unique geological features are a result of intense evaporation, leaving behind thick crusts of salt. Despite its harshness, it holds a stark beauty, offering unique insights into the geological processes that shaped the "iran geography map." #### Dasht-e Lut: A Land of Extremes Whereas the Dasht-e Lut desert is to the east, bordering Afghanistan. The Lut Desert is renowned for its extreme temperatures, holding the record for the highest surface temperature ever recorded on Earth (over 70°C or 158°F in certain areas). It is also known for its "kaluts," massive yardangs (eroded rock formations) that create an otherworldly landscape. Both the Kavir and Lut deserts are largely uninhabited, serving as stark reminders of the powerful natural forces at play across the "iran geography map." ### Climate, Seismic Activity, and Natural Heritage Iran's diverse geography leads to a wide array of climates and makes it prone to significant seismic activity. Beyond these environmental factors, the country boasts a rich natural heritage, including unique flora and fauna adapted to its varied ecosystems. #### A Tapestry of Climates Iran's climate is highly varied, ranging from arid and semi-arid in the interior and south to subtropical along the Caspian Sea coast. The mountainous regions experience cold winters with heavy snowfall, while the Persian Gulf coast has hot, humid summers. The central plateau, where the deserts lie, experiences extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night, and summer and winter. This climatic diversity supports a range of ecosystems, from lush forests to barren deserts, all contributing to the complex "iran geography map." #### Living on Active Fault Lines: Seismic Iran Iran is situated on a major seismic belt and experiences frequent earthquakes. This high level of seismic activity is due to its location at the collision zone of the Arabian, Eurasian, and Indian tectonic plates. Major fault lines crisscross the country, particularly in the mountainous regions. Understanding this aspect of Iran's geography is crucial for urban planning and disaster preparedness, as seismic activities are a constant feature of the "iran geography map." #### Flora and Fauna: Iran's Natural Treasures Despite its aridity, Iran possesses a remarkable natural heritage. The Caspian Sea region, with its higher rainfall, supports dense forests. The mountainous areas are home to various species adapted to colder climates, while the deserts host specialized flora and fauna. Notable work, such as "Flora of Iran by Pr. Ahmad Ghahreman," archived at the Wayback Machine, provides valuable insights into the country's botanical diversity. This rich biodiversity, from the unique plant life to various animal species, adds another layer of complexity and beauty to the "iran geography map." ### From Ancient Empires to Modern Provinces: A Historical Geographic Perspective The "iran geography map" is not just a static representation of landforms; it is a dynamic canvas upon which centuries of history have unfolded. From the heart of ancient Persian empires to its modern administrative divisions, geography has always dictated the flow of power, trade, and settlement. #### Mapping History: Persia (Iran), Afghanistan and Baluchistan (1897 Map) Historical maps offer a fascinating glimpse into how perceptions and delineations of Iran have evolved. For instance, "Persia (Iran), Afghanistan and Baluchistan," a map from 1897, illustrates the geopolitical landscape of the late 19th century. Such historical documents highlight the long-standing significance of Iran (then Persia) in the region, its extensive reach, and its interactions with neighboring territories. This historical context enriches our understanding of the contemporary "iran geography map" and its enduring strategic importance. Modern Iranian culture itself owes much to a renaissance in the 8th century, which was profoundly influenced by the geographic spread of knowledge and trade routes. #### Iran's Administrative Divisions: Provinces and Major Cities Modern Iran is divided into 31 provinces (ostans), each with its unique geographic features, cultural nuances, and economic activities. Exploring these significant states, provinces, and their capital cities is essential for a detailed understanding of the "iran geography map." The capital city, Tehran, is located at the foot of the Elburz Mountains in the north-central part of the country, a strategic position that has contributed to its growth as a major metropolitan center. Other major cities like Isfahan, Shiraz, Tabriz, and Mashhad are strategically located across different geographic zones, each serving as a regional hub and reflecting the diverse population distribution across the Iranian landscape. These cities are often major travel destinations and attractions, drawing visitors with their rich history and cultural heritage. ### Economic Geography: Resources and Energy The "iran geography map" is also a map of immense natural wealth. Iran is blessed with significant natural resources, particularly vast reserves of oil and natural gas, which are central to its economy and global standing. #### Underground Riches: Oil and Gas Iran holds some of the world's largest proven reserves of crude oil and natural gas. These resources are primarily concentrated in the southwestern and southern regions, particularly near the Persian Gulf. Major oil fields, such as South Pars/North Dome (shared with Qatar), are prominently marked on energy maps and contribute significantly to global energy supplies and the economies of the Gulf countries. The extraction and export of these hydrocarbons have made Iran a key player in the international energy market, profoundly influencing its geopolitical relationships and economic policies. #### Beyond Hydrocarbons: Other Natural Resources While oil and gas dominate, Iran's natural resources extend beyond hydrocarbons. The country possesses significant deposits of minerals such as copper, iron ore, lead, zinc, chromium, and coal. The mountainous terrain, particularly the Zagros and Elburz ranges, is rich in these mineral resources. The availability of these raw materials supports various industries within Iran, contributing to its industrial base and diversifying its economy beyond just oil and gas. Understanding the distribution of these resources provides a more complete picture of the economic "iran geography map." ### Exploring Iran: Travel and Cultural Geography For those interested in exploring Iran, its diverse landscape offers a wealth of opportunities, from ancient ruins to stunning natural vistas. The "iran geography map" serves as an invaluable guide for discovering its most famous travel destinations and attractions. #### Iconic Destinations and Geographic Wonders Iran's unique geography has shaped many of its most famous attractions. The historical cities like Isfahan with its stunning architecture, Shiraz with its poetic heritage, and Yazd with its desert architecture, are all nestled within distinct geographic zones. The Elburz Mountains offer opportunities for skiing and mountaineering, while the Persian Gulf islands provide warm coastal retreats. The unique landscapes of the Lut Desert, with its kaluts, are becoming increasingly popular for adventure tourism. Whether it's the ancient ruins of Persepolis, the vibrant bazaars, or the serene beauty of its natural parks, the "iran geography map" guides travelers through a journey of discovery. #### Understanding Iran: Key Facts and FAQs To further enhance understanding, here are some key facts and frequently asked questions about Iran's geography: * **Official Name:** Islamic Republic of Iran. * **Capital City:** Tehran. * **Currency:** Iranian Rial (IRR). * **Population:** Iran is the largest country in the Middle East in terms of population. * **Terrain:** Characterized by rugged terrain along the rim, with a mix of deserts and plains along the coastal areas. * **Major Deserts:** Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut. * **Major Mountain Chains:** Elburz, Kuh Rud, and Zagros. * **Coastlines:** Caspian Sea to the north; Persian Gulf, Strait of Hormuz, Gulf of Oman, and Arabian Sea to the south. * **Time Zones:** Iran Standard Time (IRST). * **Postal/Area/Zip Codes:** Specific systems apply across provinces and cities. Checking out an "iran geography map" to learn everything you want to know about this country, including its location on the world map, official symbols, seal, and flag, provides a holistic understanding of this ancient and strategically important nation. --- **Conclusion** The "iran geography map" is far more than just lines on paper; it is a vivid narrative of a nation shaped by mountains, deserts, and seas. We have journeyed across its vast 1,648,195 square kilometers, from the towering peaks of the Elburz and Zagros to the stark beauty of the Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut deserts, and along its critical northern and southern coastlines. We've seen how its strategic location at the crossroads of continents has influenced its history as the heart of the Persian Empire and its modern-day geopolitical significance, particularly concerning its immense oil and gas reserves. Understanding Iran's geography is fundamental to appreciating its rich cultural tapestry, its economic potential, and the challenges it faces, including seismic activity and climate variations. This exploration highlights the intricate relationship between the land and its people, demonstrating how physical features dictate settlement, trade, and even cultural identity. As you reflect on the insights provided, we encourage you to delve deeper. What aspects of Iran's geography surprise you the most? Share your thoughts in the comments below, and consider exploring more about this fascinating country through historical maps and detailed atlases, such as those from Infoplease or large laminated maps of Asia that showcase its physical features in detail. The journey to understand Iran truly begins with its magnificent and complex geography.

Where is Iran?, Where is Iran located?
Fordow Iran Map Pictures | Download Free Images on Unsplash
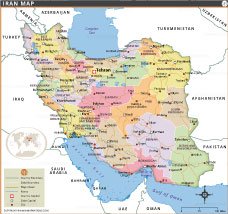
Where is Iran?, Where is Iran located?