Syria, Russia, Iran: Unraveling A Complex Alliance
The geopolitical landscape of the Middle East is a tapestry woven with intricate alliances, shifting interests, and enduring conflicts. At its heart lies Syria, a nation that has, for over a decade, been a crucible where the strategic ambitions of major regional and global powers, particularly Russia and Iran, have converged and clashed. This article delves into the multifaceted relationship between Syria, Russia, and Iran, exploring their shared objectives, evolving dynamics, and the profound impact of their collaboration on the region and beyond. From military interventions to economic pressures and diplomatic maneuvers, understanding this tripartite relationship is crucial for grasping the current state of affairs in the Levant and anticipating future developments.
The Syrian conflict, which began as a domestic uprising, quickly escalated into a proxy war, drawing in numerous international actors. Among the most steadfast supporters of President Bashar al-Assad's government have been Russia and Iran. Their involvement has been pivotal in shaping the conflict's trajectory, preventing the collapse of the Syrian regime, and establishing a significant foothold in a strategically vital region. However, their alliance is not without its complexities, marked by both deep cooperation and occasional divergences in interests, especially as the conflict evolves and new global events reshape their individual priorities.
Table of Contents
- The Genesis of a Strategic Convergence
- Military Intervention and the Turning Point of 2015
- Evolving Roles and Shifting Dynamics
- The Campaign to Expel US Forces
- Diplomatic Avenues: The Astana Process
- Syria's Path to International Recognition
- Challenges and Tensions Within the Alliance
- The Future of the Syria, Russia, Iran Axis
The Genesis of a Strategic Convergence
The relationship between Syria, Russia, and Iran is rooted in a shared strategic interest in maintaining the Assad regime and countering Western influence in the Middle East. For years, both Russia and Iran have been steadfast supporters of Syrian President Bashar Assad. This support solidified into a robust alliance as the Syrian civil war intensified, threatening the very existence of the government in Damascus. The convergence of Iranian and Russian strategic interests in Syria became particularly evident as the war progressed, especially in 2015.
Prior to 2015, Iran had already established a significant presence in Syria, providing military advisors, financial aid, and mobilizing proxy forces like Hezbollah to bolster the regime. Russia, while a long-standing ally, initially played a more diplomatic role. However, as opposition forces gained significant ground, including launching an offensive against the Syrian government, the calculus shifted. Both powers recognized that a collapse of the Assad regime would represent a major strategic defeat, opening the door for hostile forces and potentially disrupting the regional balance of power in favor of their adversaries. This realization led to a more forceful intervention, transforming the conflict's dynamics.
Military Intervention and the Turning Point of 2015
The year 2015 marked a critical juncture in the Syrian conflict. Faced with the imminent threat of an opposition victory, both Russia and Iran stepped in forcefully. Russia carried out airstrikes in Syria after rebels launched an offensive against the Syrian government, providing crucial air cover that the Syrian army desperately needed. This direct military intervention by Moscow was a game-changer, allowing the Syrian armed forces to regain lost territory and shift the momentum of the war. Concurrently, Iran continued to reinforce its ground presence, coordinating with various militias and providing logistical support, effectively creating a multi-layered defense for the regime.
The combined military might and strategic coordination of Russia and Iran proved instrumental in preventing the collapse of the Syrian government. Russian air power, coupled with Iranian-backed ground forces, created a formidable front that systematically pushed back rebel groups and extremist organizations. This period showcased the operational synergy between the two external powers, with Russia focusing on aerial superiority and strategic bombing, while Iran concentrated on ground operations, training, and the deployment of proxy forces. This division of labor, though not always seamless, was highly effective in securing key territories and protecting vital infrastructure, ensuring the survival of the Assad government against overwhelming odds.
Evolving Roles and Shifting Dynamics
While the core objective of supporting Bashar al-Assad has remained constant, the specific roles and dynamics within the Syria, Russia, and Iran alliance have evolved significantly over time. The initial phase was characterized by a desperate effort to save the regime. As the war progressed and the regime's position stabilized, the focus shifted towards consolidating gains, managing regional influence, and addressing the presence of other international actors.
Russia's Post-2022 Stance
A notable shift in Russia’s approach to Iran in Syria has occurred dramatically since its invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Moscow previously balanced between Iran and Israel, attempting to maintain good relations with both while pursuing its own strategic interests in Syria. This delicate balancing act allowed Russia to mediate tensions and present itself as a regional power broker. However, the demands of the war in Ukraine have seemingly altered this equilibrium. Russia has become, I'd say, more brazen since 2022 in pushing back against the U.S. presence in northeast Syria, indicating a more confrontational stance over Syria. This change suggests a re-prioritization of Russian foreign policy, where challenging perceived Western hegemony, including in Syria, takes precedence, potentially leading to a closer alignment with Iran against common adversaries.
Interestingly, the relationship between Russia and Iran has also seen nuances regarding other international agreements. For instance, Iran and the JCPOA is another example where, before 2022, when the Biden administration tried to find a pathway back into a restored nuclear deal, Russia was quite helpful. This indicates that while their strategic interests in Syria are deeply intertwined, their cooperation can extend to other geopolitical arenas, albeit with shifts influenced by broader global events.
Iranian Strategic Imperatives
For Iran, Syria represents a vital link in its regional network, providing a strategic depth and a land bridge to Hezbollah in Lebanon. Breaking Iran’s regional network has been a major goal for Israel, highlighting the immense strategic value of Syria to Tehran. The presence of Iranian-backed forces in Syria allows Iran to project power, deter potential aggressors, and counter the influence of rivals like Saudi Arabia and Israel. Furthermore, Iran's involvement in Syria is also a response to its own international isolation. For Iran, international sanctions over its advancing nuclear program have ground down its economy, making regional alliances and strategic depth even more critical for its security and survival.
The Campaign to Expel US Forces
A significant shared objective for Syria, Russia, and Iran has been the expulsion of US forces from Syrian territory. The presence of American troops, particularly in eastern Syria, is viewed by the tripartite alliance as an illegal occupation and a direct impediment to the full restoration of Syrian sovereignty. Beginning on July 7, Iran, Russia, and the Syrian regime surged forces to eastern Syria while accelerating their campaign to expel US forces from Syria. This campaign has been multi-faceted, employing a combination of military pressure, information operations, and grassroots mobilization.
The alliance has actively engaged in spreading information operations, aiming to delegitimize the US presence and rally public opinion against it. This includes disseminating narratives that portray American forces as occupiers and highlighting any negative impacts of their presence. Concurrently, efforts have been made to grow a grassroots movement, encouraging local populations to protest and demand the withdrawal of US troops. At the senior level, regular meetings for operational planning ensure a coordinated approach to achieving this objective. This concerted effort underscores the alliance's determination to remove what they perceive as a foreign impediment to their strategic goals in the region.
Diplomatic Avenues: The Astana Process
Beyond military and political coordination, Russia, Iran, and Turkey have also engaged in diplomatic efforts to resolve the Syrian crisis, primarily through the Astana Process. The foreign ministers of Russia, Iran, and Turkiye attend a meeting on the crisis in Syria in the framework of the Astana Process on the sidelines of the Doha Forum in Doha, Qatar, December 7, 2024. This forum serves as a platform for the three guarantor states to discuss ceasefires, de-escalation zones, humanitarian aid, and the political future of Syria. While Turkey's interests sometimes diverge from those of Russia and Iran, particularly regarding Syrian opposition groups, the Astana Process provides a crucial channel for dialogue and coordination, preventing wider conflicts and managing the complex dynamics on the ground.
The Astana Process highlights the pragmatic nature of the alliances in Syria. Despite their differences, these powers recognize the need for a diplomatic track to complement military actions. It also signifies Russia's role as a key mediator and convener in the region, capable of bringing together diverse actors to discuss the future of Syria. This diplomatic engagement, alongside military support, forms a comprehensive strategy for managing the Syrian conflict and shaping its outcome.
Syria's Path to International Recognition
As the conflict has subsided in many areas and the Assad regime has consolidated control, there has been a noticeable shift in Syria's international standing. The new Syrian authorities are rapidly moving toward international recognition, and not just among their regional neighbors. This is a significant development, indicating a gradual acceptance of the current reality on the ground by various international actors. Regional normalization efforts, particularly from Arab states, have paved the way for Syria's reintegration into regional bodies like the Arab League.
Western Sanctions and Their Impact
Paradoxically, even the United States and the European Union have lifted most of the sanctions earlier imposed on Damascus, keen to limit the influence in Syria of the previous regime’s allies Iran and Russia. This move reflects a complex geopolitical calculation. While Western powers initially sought to isolate the Assad regime, the prolonged conflict and the entrenched presence of Russia and Iran have led to a re-evaluation of strategies. Lifting some sanctions could be seen as an attempt to create space for Western influence, facilitate humanitarian aid, or simply acknowledge the new political reality, rather than a full endorsement of the regime.
However, the broader context of sanctions remains a critical factor. For Iran, international sanctions over its advancing nuclear program have ground down its economy, making its strategic alliances and regional influence even more vital. The lifting of some sanctions on Syria, therefore, might also be viewed through the lens of easing pressure on Iran's key regional partner, indirectly benefiting Tehran's economic and strategic resilience.
Israel's Regional Security Concerns
For Israel, breaking Iran’s regional network has been a major goal, though it is wary over jihadi fighters among the insurgents who toppled Assad. Israel views Iran's growing military presence and influence in Syria, particularly through Hezbollah and other proxy groups, as a direct threat to its security. Consequently, Israel has conducted numerous airstrikes in Syria, targeting Iranian assets and arms shipments. This ongoing shadow war adds another layer of complexity to the Syrian landscape, as Russia often finds itself in a delicate position, balancing its security coordination with Israel with its strategic alliance with Iran and Syria.
Challenges and Tensions Within the Alliance
Despite their shared objectives, the alliance between Syria, Russia, and Iran is not without its internal challenges and tensions. By early 2024, both Iran and Russia had changed when it came to the Syrian president. This indicates a growing frustration or shift in expectations regarding Bashar al-Assad's leadership and his approach to post-conflict governance. Russia was particularly incensed by his repeated violations of the Idlib de-escalation agreement and stubborn resistance to any form of a negotiated settlement. This highlights a divergence in strategic priorities: while Russia seeks a more stable and internationally recognized political solution, Assad's uncompromising stance can complicate these efforts.
These internal frictions underscore the transactional nature of the alliance. While united against common adversaries and in preserving the regime, Russia and Iran also pursue their distinct national interests. Russia aims to solidify its long-term military presence and influence in the Mediterranean, while Iran seeks to secure its land bridge to Lebanon and expand its regional network. Syria, in turn, seeks to leverage the support of both powers to restore its sovereignty and reconstruct the country. Managing these sometimes-conflicting interests requires continuous high-level engagement, as demonstrated by the call between Russia’s President, Vladimir V. Putin, and President Masoud Pezeshkian of Iran, where the two leaders expressed “unconditional support” for Syria’s government, calling the. This kind of diplomatic outreach is essential to reaffirm unity and address any emerging disagreements.
The Future of the Syria, Russia, Iran Axis
The future of the Syria, Russia, and Iran axis remains a critical factor in the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East. Having successfully prevented the collapse of the Assad regime and consolidated their influence, the alliance now faces new challenges, including post-conflict reconstruction, managing regional rivalries, and navigating the complexities of international recognition. The continued presence of US forces, Israel's security concerns, and the evolving global dynamics post-2022 will all shape the trajectory of this powerful triumvirate.
Their enduring cooperation, rooted in shared strategic interests and a common desire to counter Western influence, suggests that this alliance will remain a formidable force in the region. However, internal tensions and the individual national interests of each player will continue to test its cohesion. As Syria moves towards a new phase of stability, the roles of Russia and Iran will likely shift from active military intervention to more long-term strategic partnerships, focusing on economic ties, security cooperation, and political influence. The intricate dance between these three nations will continue to be a defining feature of Middle Eastern politics for years to come.
The complex relationship between Syria, Russia, and Iran is a testament to the fluid nature of international relations. From a desperate fight for survival to a strategic consolidation of power, their alliance has reshaped the Middle East. Understanding the nuances of their cooperation and competition is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the region's past, present, and future. What are your thoughts on the evolving dynamics of this powerful alliance? Share your insights in the comments below, or explore our other articles on Middle Eastern geopolitics for more in-depth analysis.
- Iran Sexse
- Iran Population Fast Fact
- Hijab In Iran
- Iran Threatens Israel
- Former Nato Commander Cites Trumps Influence On Iran Hezbollah Ceasefire
Political Map of Syria - Nations Online Project

History of Syria | Britannica
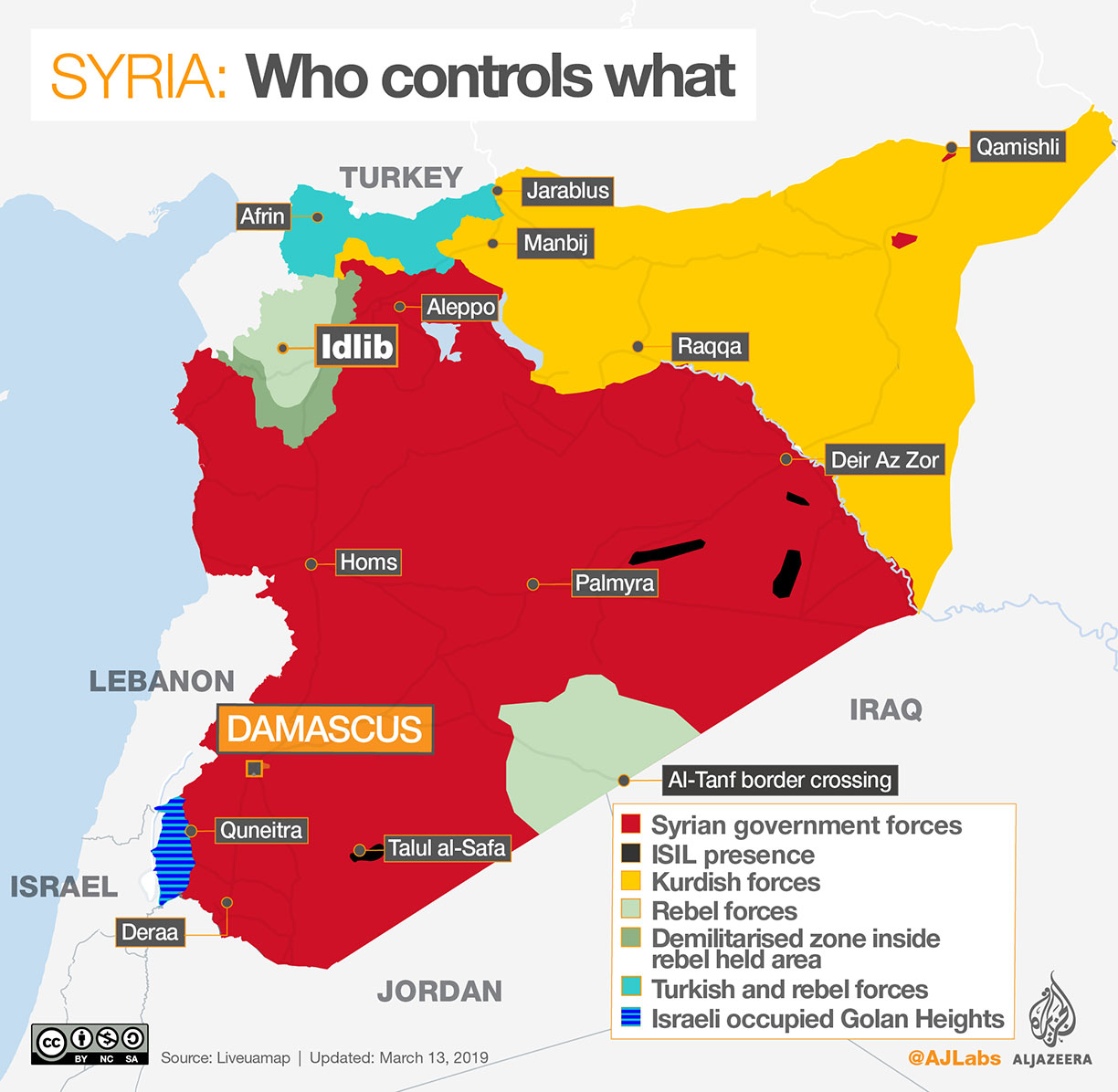
Political Map of Syria - Nations Online Project