Navigating Air Quality In Iran: Your Essential AQI Guide
Iran, a country strategically located in Western Asia, shares borders with nations like Iraq, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, making it a pivotal region both geographically and economically. With a population of 83.2 million people as of 2018, its urban centers are bustling hubs of activity, but this rapid urbanization and industrialization often come with significant environmental challenges, particularly concerning air quality. Understanding the Air Quality Index (AQI) in Iran is not just a matter of environmental curiosity; it's a critical component of public health and daily decision-making for millions of its citizens.
The capital city, Tehran, stands out as an important economic and cultural center, home to over 8.8 million inhabitants, making it one of the largest cities in West Asia. Such dense population and intense economic activity naturally contribute to air pollution, necessitating robust monitoring and public awareness campaigns. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of AQI in Iran, exploring its measurement, impact on daily life, and the ongoing efforts to manage and mitigate air pollution across the nation.
Table of Contents
- Understanding AQI Iran: A Vital Health Metric
- The Geographic and Demographic Context of Air Pollution in Iran
- Decoding Air Quality Index Standards: Global vs. Local
- Real-time AQI in Iran's Major Cities: A Snapshot
- The Practical Application of AQI Data for Daily Life
- Iran's National Efforts in Air Quality Monitoring
- Challenges and Future Outlook for AQI Iran
- Empowering Yourself with Air Quality Information
Understanding AQI Iran: A Vital Health Metric
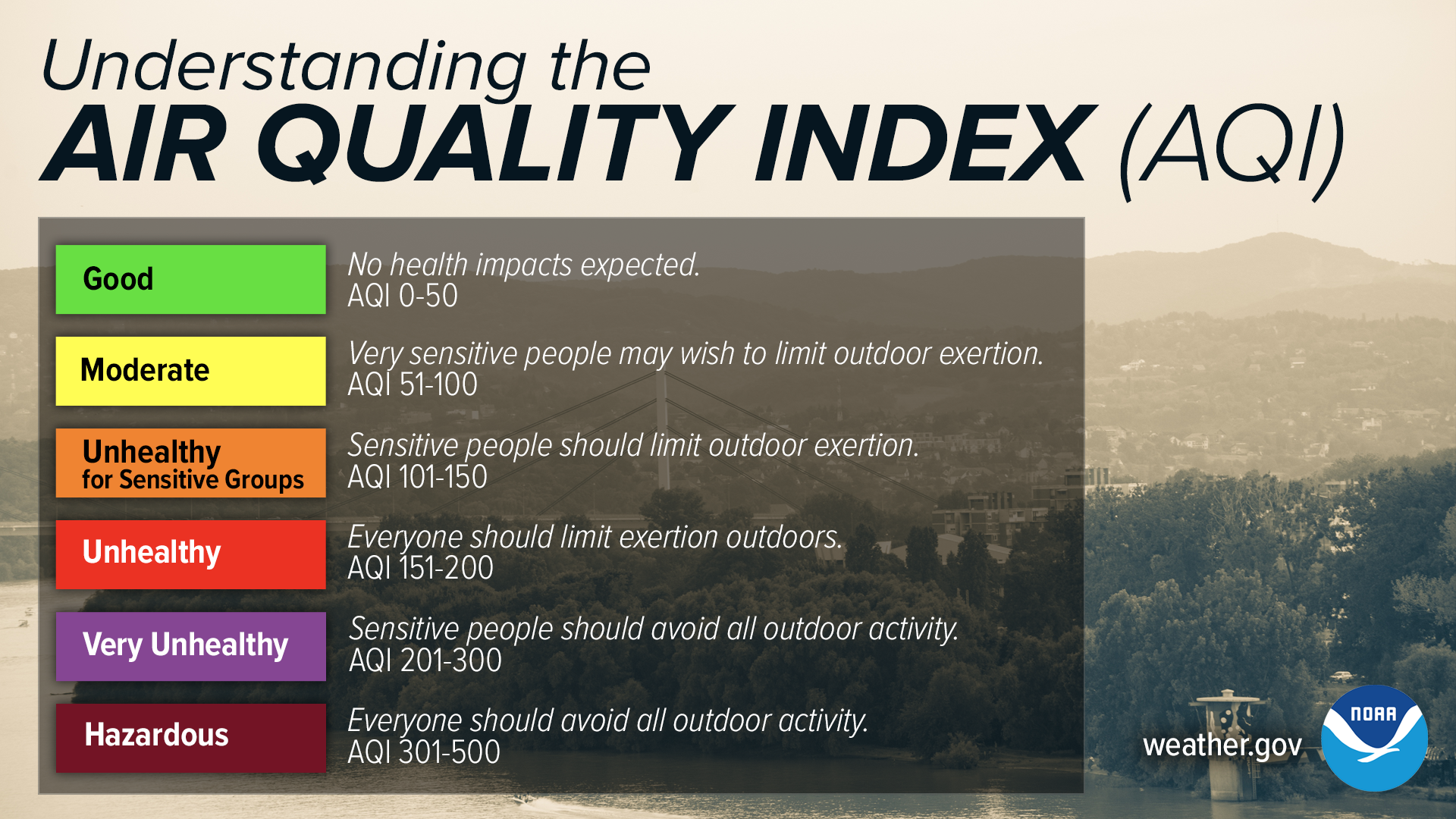
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a standardized measure used by government agencies to communicate how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. It tells you what associated health effects might be a concern for you. A higher AQI value indicates a greater level of air pollution and, therefore, a greater health concern. For a country like Iran, where air pollution can frequently reach concerning levels, understanding the AQI is paramount for public health. The AQI typically focuses on key air pollutants such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Each of these pollutants has different health impacts, and the AQI consolidates their levels into a single, easy-to-understand number.
- Breaking News Israel Attacks Iran Today
- Who Would Win Israel Vs Iran
- Iran Cuisine Recipes
- Iran Hostage Situation
- Flights To Iran
When we talk about the AQI Iran, we are referring to the specific measurements and forecasts applicable to various cities and regions within the country. This data empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their daily activities, especially those involving outdoor exposure. For instance, on days with high AQI readings, it might be advisable to limit strenuous outdoor exercise or for sensitive groups to stay indoors. This direct link between environmental data and personal well-being underscores why the AQI is a vital health metric, not just an environmental statistic.
The Geographic and Demographic Context of Air Pollution in Iran
Iran's diverse geography, ranging from arid deserts to mountain ranges, plays a significant role in its air quality dynamics. Mountain ranges can trap pollutants, creating inversions that prevent dispersion, while desert areas can contribute to dust storms, adding to particulate matter in the air. The country's rapid urbanization and industrial growth, particularly in its major cities, are primary drivers of air pollution. As mentioned, Iran has 83.2 million people, a substantial portion of whom reside in urban areas, intensifying the concentration of pollution sources.
Sources of air pollution in Iran are varied and include vehicular emissions, industrial activities, power plants, and residential heating. The quality of fuel, the age of vehicle fleets, and the type of industrial processes all contribute to the overall air pollution burden. Understanding this complex interplay between geography, demography, and economic activity is crucial for comprehending the challenges of managing AQI Iran.
- Israel Vsiran
- Iran Armed Forces Vs Israel
- Iran Vs Israel War 2023
- Iran Vs Israel Wars
- Iran Vs Israel Military Who Would Win
Tehran: The Epicenter of Air Quality Challenges
Tehran, the sprawling capital, is often at the forefront of discussions about air pollution in Iran. With over 8.8 million inhabitants, it is one of the largest cities in West Asia and a major economic and cultural hub. This density, combined with its unique geographical setting – nestled at the foot of the Alborz mountains – creates a perfect storm for air quality issues. The mountains can act as a barrier, trapping pollutants within the city basin, especially during colder months when temperature inversions are common.
The sheer volume of vehicles on Tehran's roads is a primary contributor to its high AQI readings. Traffic congestion is chronic, leading to prolonged emissions from idling engines. Additionally, industrial zones surrounding the city and the use of older, less efficient heating systems in residential areas further exacerbate the problem. Monitoring the Tehran Air Quality Index (AQI) is a daily routine for many residents, as the city frequently experiences days categorized as unhealthy or even hazardous, impacting everything from school closures to public health advisories.
Decoding Air Quality Index Standards: Global vs. Local
It's important to recognize that while the concept of an Air Quality Index is universal, the specific scales and pollutant thresholds can vary between countries. Different nations and regions adopt their own AQI scales, often tailored to their specific environmental conditions and public health priorities. For instance, you might encounter references to AQI (US), AQC (Australia), AQHI (Canada), AQI (China), or AQI (Netherlands). While these systems all aim to communicate air quality information, their numerical values for the same level of pollution might differ, making direct comparisons challenging without understanding the underlying standard.
In Iran, the national monitoring system, known as "سامانه پایش کیفی هوای کشور" (National Air Quality Monitoring System), operates to supervise and control air quality across the country. This system likely adheres to specific national standards, which may be based on or aligned with international guidelines, but are ultimately designed for the Iranian context. When checking the AQI Iran, it's generally understood to be reported based on these national standards, often with a clear indication if a common international standard, like the US EPA's AQI, is being used for broader comparability. For example, a report might state "AQI (US) 53 Moderate," indicating the US standard is being applied for that specific reading.
Real-time AQI in Iran's Major Cities: A Snapshot
Access to real-time air quality information is crucial for residents across Iran. Various platforms and applications provide localized air quality index and forecasts for major cities, allowing people to track air pollution and make healthier lifestyle decisions. This real-time broadcasting of air quality information is available on phones for more than 180 countries, including Iran, thanks to global air quality monitoring projects like AirVisual and the World Air Quality Index project.
Let's look at some examples from the provided data, which highlight the varying conditions across Iran's urban centers:
- Tehran: As discussed, the Tehran Air Quality Index (AQI) is frequently monitored due to its consistently challenging air quality. Localized forecasts help residents plan their day, deciding whether to engage in outdoor activities or take precautions.
- Esfahan: The data indicates, "Esfahan Air Quality Index (AQI) is now moderate." This suggests periods where the air quality is acceptable, though it can fluctuate. Reading the air pollution in Esfahan, Iran with services like AirVisual provides up-to-date information for residents. A "moderate" reading, such as "AQI (US) 53 Moderate," means air quality is acceptable; however, for some pollutants, there may be a moderate health concern for a very small number of people who are unusually sensitive to air pollution.
- Ahvaz: The situation in Ahvaz can be more severe, with reports stating, "Ahvaz Air Quality Index (AQI) is now unhealthy for sensitive groups." This indicates a significant health risk for individuals with respiratory or heart disease, children, and older adults. Even healthy individuals may experience minor effects. Monitoring the air pollution in Ahvaz, Iran, is particularly vital for vulnerable populations.
- Qom: While specific status isn't provided in the data, the mention of "Qom Air Quality Index (AQI)" implies that Qom, another significant city, also has its air quality regularly monitored and reported.
These examples underscore the dynamic nature of air quality across Iran and the necessity of real-time data for public awareness and protection.
Esfahan: A City with Fluctuating Air Quality
Esfahan, renowned for its historical architecture and vibrant culture, also faces its share of air quality challenges. While the provided data notes "Esfahan Air Quality Index (AQI) is now moderate," this status can shift rapidly depending on meteorological conditions, traffic volume, and industrial activity. The city's growth and industrial presence contribute to emissions, which, combined with geographical factors, can lead to periods of elevated pollution. Residents and visitors in Esfahan rely on up-to-date AQI information to decide on outdoor activities, especially during peak pollution times or seasons.
Ahvaz: Addressing Persistent Air Quality Concerns
Ahvaz, a major city in southwestern Iran, frequently experiences some of the most severe air pollution levels globally, often due to a combination of industrial emissions, vehicular traffic, and natural dust storms originating from the surrounding desert regions. The report that "Ahvaz Air Quality Index (AQI) is now unhealthy for sensitive groups" highlights a recurring issue for the city. This classification means that people with lung disease, older adults, and children are at greater risk from the presence of ozone in the air, while those with heart or lung disease, older adults, and children are at greater risk from the presence of particles in the air. The persistent nature of high AQI readings in Ahvaz necessitates ongoing public health advisories and long-term environmental strategies.
Qom: Monitoring Air Quality in a Sacred City
Qom, a significant religious center in Iran, also has its air quality continuously monitored. While specific details on its current AQI status weren't provided in the given data, the fact that "Qom Air Quality Index (AQI)" is tracked indicates its importance within the national air quality monitoring network. Like other urban areas, Qom faces challenges from vehicle emissions and local industrial activities. Reliable AQI data for Qom helps protect its residents and the many pilgrims who visit the city throughout the year, ensuring they are aware of potential health risks related to air pollution.
The Practical Application of AQI Data for Daily Life
The ultimate goal of monitoring and broadcasting the AQI Iran is to empower individuals to make healthier lifestyle decisions. Knowing the current and forecasted air quality can significantly impact daily planning. Here's how people can use this information:
- Planning Outdoor Activities: On days with high AQI, it's advisable to reduce prolonged or heavy exertion outdoors. This is especially true for sensitive groups. For example, if the AQI for Tehran is "unhealthy," outdoor sports events might be postponed, and individuals might opt for indoor exercise.
- Protecting Vulnerable Populations: Parents of children, caregivers for the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions can use AQI data to decide whether to limit outdoor exposure for these sensitive groups.
- Commuting Decisions: Commuters might choose public transport over driving on high pollution days to reduce their personal exposure and contribution to emissions.
- Using Air Purifiers: In areas with consistently poor air quality, knowing the AQI can inform decisions about using indoor air purifiers more frequently or ensuring proper ventilation.
- Health Precautions: On days with particularly high AQI, wearing N95 masks outdoors can offer some protection against particulate matter.
The availability of real-time air quality information on mobile phones for over 180 countries, including Iran, makes this practical application accessible to a wide audience. Services that provide localized air quality index and forecasts, such as those mentioned, are invaluable tools for public health.
Iran's National Efforts in Air Quality Monitoring
Recognizing the severity of air pollution, the Iranian government has established and maintains a national air quality monitoring system. The "سامانه پایش کیفی هوای کشور" (National Air Quality Monitoring System) is a crucial initiative operating across the country. Its primary objective is to supervise and control air quality, providing the necessary data for policy-making, public advisories, and environmental management. This system collects data from numerous monitoring stations located in urban and industrial areas, processing it to generate the Iran Air Quality Index (AQI) reports that are then disseminated to the public.
The existence of such a centralized system demonstrates a commitment to addressing air quality issues. However, the effectiveness of these efforts relies not only on data collection but also on the implementation of regulations, promotion of cleaner technologies, and public awareness campaigns. The data provided by this national system forms the backbone of understanding the overall air quality landscape in Iran and guiding future interventions.
Challenges and Future Outlook for AQI Iran
Despite monitoring efforts and increasing public awareness, Iran faces significant challenges in achieving consistently healthy air quality across its urban centers. These challenges are multifaceted:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many vehicles and industrial facilities are older and less fuel-efficient, leading to higher emissions.
- Fuel Quality: The quality of fuel used in vehicles and industries can directly impact pollutant emissions.
- Urban Planning: Rapid and sometimes unplanned urban expansion can exacerbate traffic congestion and limit green spaces.
- Meteorological Factors: Specific geographical features and weather patterns, such as temperature inversions in mountainous cities like Tehran or dust storms in the southwest, can trap or transport pollutants.
- Economic Sanctions: International sanctions can hinder access to advanced pollution control technologies and cleaner energy sources.
Looking ahead, the future of AQI Iran depends on a concerted effort involving various stakeholders. This includes investing in public transportation, promoting electric vehicles, upgrading industrial facilities with cleaner technologies, improving fuel quality, and implementing stricter emission standards. International cooperation and sharing of expertise can also play a vital role in addressing these complex environmental issues. Public participation and awareness will continue to be critical in advocating for and supporting these necessary changes.
Empowering Yourself with Air Quality Information
While large-scale policy changes are essential for long-term improvement, individual awareness and action remain incredibly powerful. The availability of real-time AQI data, whether through dedicated apps or websites, puts vital information directly into the hands of the public. The World Air Quality Index project, for instance, emphasizes that while it exercises "all reasonable skill and care in compiling the contents of this information," users should understand that no entity can be held liable for any direct or indirect loss or injury arising from the data's supply. This disclaimer underscores the importance of using such data responsibly and in conjunction with official health advisories.
By regularly checking the AQI Iran for your specific location, you can proactively protect your health and contribute to broader awareness. Sharing this information with family and friends, especially those in sensitive groups, helps build a more health-conscious community. Your engagement with air quality data is a step towards a healthier future for yourself and for Iran.
Conclusion
Understanding the Air Quality Index in Iran is more than just interpreting numbers; it's about recognizing a critical public health issue and empowering individuals to make informed decisions for their well-being. From the bustling streets of Tehran to the historical sites of Esfahan and the industrial hubs of Ahvaz, air quality remains a significant concern, shaped by a complex interplay of geography, demographics, and economic activity.
While challenges persist, Iran's national monitoring efforts and the increasing accessibility of real-time data provide crucial tools for managing this issue. By staying informed about the AQI Iran, utilizing available resources, and supporting initiatives for cleaner air, each individual plays a part in fostering a healthier environment. We encourage you to regularly check the air quality for your city and share this vital information with your community. What are your experiences with air quality in Iran? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, or explore other articles on our site for more insights into environmental health.
Chart_US.png)
Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 And AQI Levels - Vision
Air Quality Infographics

Understanding the Air Quality Index (AQI) and How it Works