Bahrain Iran Map: Unraveling Geopolitical Tensions & Connections
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Understanding the Bahrain Iran Map
- Geographical Proximity: A Closer Look at the Bahrain Iran Map
- Historical Ties and Iranian Claims on Bahrain
- Strained Relations Since the 1979 Revolution
- Geopolitical Flashpoints and Regional Stability
- US Military Presence and Regional Dynamics
- Understanding the Map: Tools and Projections
- Travel Advisories and Regional Caution
- Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Geopolitical Landscape
Introduction: Understanding the Bahrain Iran Map
The intricate relationship between Bahrain and Iran is a cornerstone of Middle Eastern geopolitics, often best understood by examining the Bahrain Iran map. This geographical proximity, while seemingly straightforward, belies a complex tapestry of historical ties, cultural influences, and, more recently, deep-seated geopolitical tensions. Understanding the contours of this relationship is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the broader dynamics of the Gulf region.
From shared maritime borders to centuries of intertwined history, the connection between these two nations is undeniable. However, as we will explore, the period since the 1979 Iranian Revolution has seen their bilateral relations become increasingly strained, marked by ideological differences and regional power struggles. This article delves into the various facets of the Bahrain Iran map, providing a comprehensive overview of their geographical, historical, and geopolitical connections.
Geographical Proximity: A Closer Look at the Bahrain Iran Map
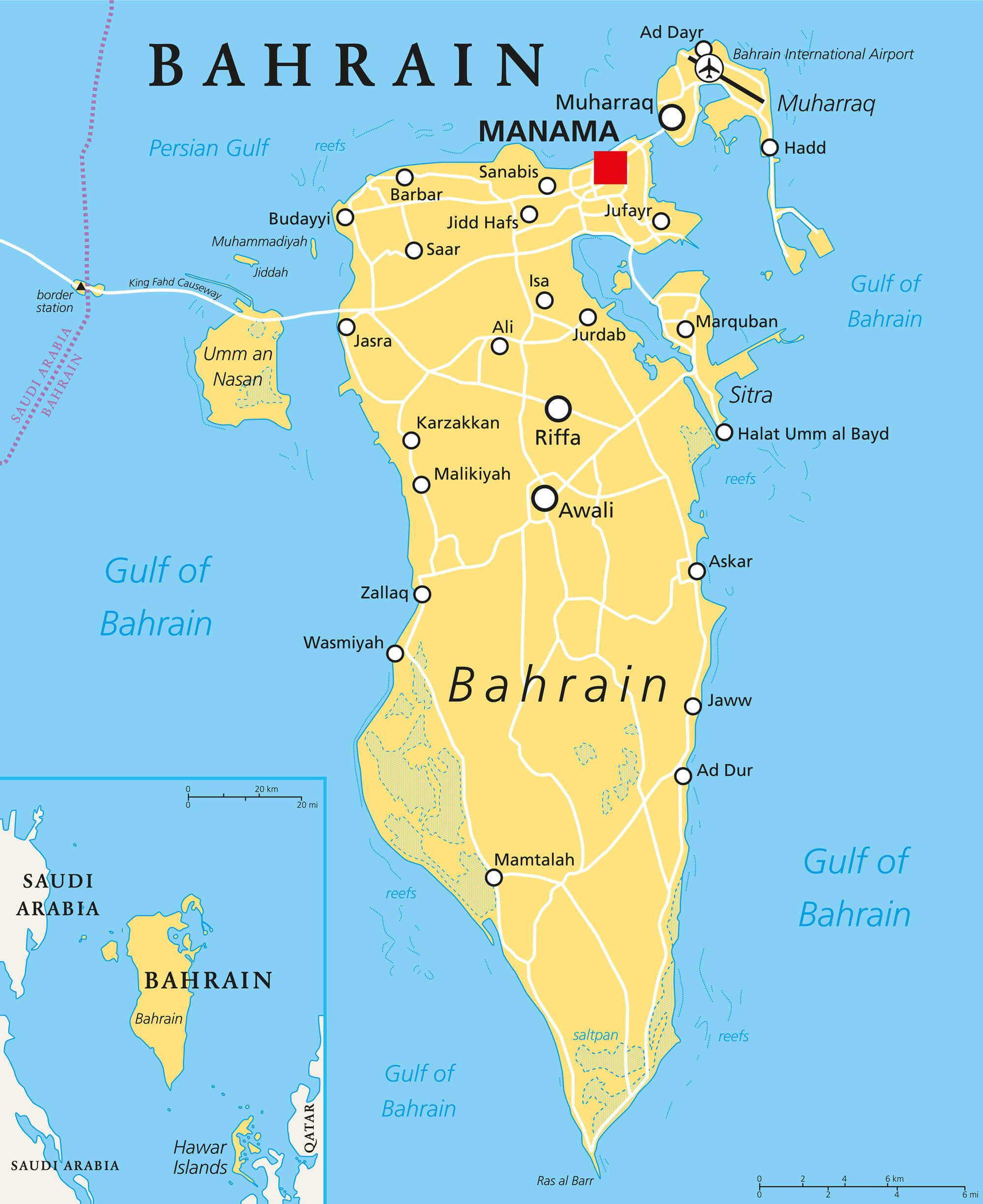
When one observes the Bahrain Iran map, the immediate impression is one of significant geographical closeness. Bahrain, an archipelago nation, is strategically located in the Persian Gulf (also known as the Arabian Gulf). Its position is critical, sharing its maritime borders not only with Iran but also with Qatar and Saudi Arabia. The outline map representing the country of Bahrain in the Middle East clearly shows its main island, Al Bahrayn (the largest island), surrounded by numerous smaller islands, all situated in a vital waterway.
- Israel Iran Nuclear
- Iran Nickname
- American And Iran War
- Iran Vs Israel Drones
- Who Would Win In A War Israel Vs Iran
The physical distance between the two nations underscores their inherent connection. The air travel (bird fly) shortest distance between Bahrain and Iran is 768 kilometers, which translates to approximately 477 miles. This short distance means that if one were to travel by airplane, with an average speed of 560 miles per hour, it would take a mere 0.85 hours to arrive. This extreme proximity has historically facilitated interaction but has also amplified the impact of political disagreements, making the Bahrain Iran map a focal point for regional stability.
Historical Ties and Iranian Claims on Bahrain
The history between Bahrain and Iran is long and complex, extending far beyond modern political boundaries. For centuries, the two entities have been intertwined, with periods of direct Iranian influence over the island nation. This historical context is vital for understanding the underlying currents that continue to shape the Bahrain Iran map today.
Early Domination and Parliamentary Representation
One of the most significant historical periods saw Iran dominating the island of Bahrain from 1602 to 1783. This prolonged period of control left an indelible mark on Bahrain's cultural and demographic landscape. Even after this direct rule ended, Iran continued to assert claims over Bahrain for many years. Notably, from 1906 to 1971, Iran went as far as reserving two seats for Bahrain in its parliament, treating it as its 14th province. This act, while never internationally recognized as legitimate, illustrates the depth of Iran's historical claim and its perception of the Bahrain Iran map.
The Post-British Withdrawal Era
The issue of Bahrain's sovereignty came to a head in the early 1970s. As the British began to withdraw from areas east of the Suez Canal by 1971, the last Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, raised the Bahrain issue with them. Ultimately, a United Nations-sponsored referendum was held, which overwhelmingly favored Bahraini independence. Despite Iran's historical claims, it accepted the results, leading to Bahrain's full independence in 1971. This moment marked a formal shift in the Bahrain Iran map, from a claimed province to an independent sovereign state, though the historical memory of Iranian claims persists.
Strained Relations Since the 1979 Revolution
While bilateral relations existed between Bahrain and Iran for a long time, a profound shift occurred following the 1979 Iranian Revolution, which saw Ayatollah Khomeini come to power. Since this pivotal event, diplomatic relations between the two countries have been consistently strained. This period marks a critical turning point on the Bahrain Iran map, transforming a complex historical relationship into one dominated by geopolitical friction.
The reasons for this strain are multifaceted, encompassing various geopolitical issues. Key among these are differing interpretations of Islam, particularly the Sunni-Shiite divide, which has significant implications given Bahrain's Shiite majority population ruled by a Sunni monarchy. Furthermore, the "awakening of the Islamic world" as envisioned by the Iranian revolution, and starkly contrasting relations with the United States, Europe, and other Western countries, have further widened the ideological chasm. These deep-seated disagreements have led to periods of diplomatic rupture, accusations of interference, and a general climate of mistrust that continues to define the Bahrain Iran map today.
Geopolitical Flashpoints and Regional Stability
The Bahrain Iran map is not merely a representation of geography; it's a canvas upon which complex geopolitical flashpoints are played out. The region, often referred to as the Middle East, is vast, representing an area of more than five million square miles and including states like Egypt, Oman, Yemen, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Iran, Bahrain, Syria, Jordan, Turkey, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, and Israel. Within this intricate web, the relationship between Bahrain and Iran is a critical indicator of broader regional stability, often influenced by external powers and internal conflicts.
The Israel-Iran Conflict's Wider Reach
One of the most significant factors influencing the Bahrain Iran map is the ongoing, undeclared conflict between Israel and Iran. This conflict extends well beyond the borders of both countries, creating ripple effects across the entire Middle East. For instance, Israel, under "Operation Rising Lion," has launched airstrikes and drone attacks on Iran’s nuclear and military sites, including Tehran, the Natanz uranium enrichment facility, a nuclear research center, two military bases in Tabriz, and an underground missile storage site in Kermanshah, all aimed at preventing Iran from advancing towards building an atomic weapon. Iran, in turn, has reported at least 224 deaths in Israeli attacks, mostly civilians, though this toll has not been updated for days.
This broader conflict has direct implications for Gulf states like Bahrain. A potential regional war, fueled by these tensions, could significantly impact Iraq, Kuwait, and Bahrain if Iran decides to escalate. The interconnectedness means that an attack on Iranian interests, or an Iranian retaliation, could easily spill over, affecting maritime routes, energy supplies, and overall security in the Gulf, placing the Bahrain Iran map at the center of potential regional instability.
Maritime Security Concerns in the Gulf
The Persian Gulf and the Oman Sea are crucial international waterways for global trade, particularly for oil shipments. Given their geographical proximity, the Bahrain Iran map highlights the vulnerability of these waters to regional tensions. Iran has explicitly warned that a conflict zone exists over international waters in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea within the Tehran FIR (Flight Information Region) due to military activity. This warning raises significant risks for maritime and air traffic near Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and the UAE. The presence of navy vessels leaving a key port in the Middle Eastern country of Bahrain as Washington braces for a potential Iranian strike underscores the immediate and tangible threat to maritime security and the potential for rapid escalation.
US Military Presence and Regional Dynamics
The United States maintains a significant military presence in the Middle East, a factor that profoundly influences the geopolitical dynamics observed on the Bahrain Iran map. This presence is primarily aimed at safeguarding regional stability, counteracting extremist threats, and, crucially, containing Iranian influence. A look at US military bases in the Middle East reveals their strategic positioning, particularly as Iran threatens strikes from Syria on the Mediterranean coast, through Iraq, and onto Gulf states of Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates.
Bahrain hosts a major US naval base, serving as the headquarters for the U.S. Fifth Fleet. This makes Bahrain a critical node in Washington's regional security architecture and, by extension, a potential target or staging ground in any escalated conflict involving Iran. The presence of these bases, while intended to deter aggression, also means that countries like Bahrain are inevitably drawn into the broader strategic competition between the US and Iran. This complex interplay of alliances and rivalries is a constant feature of the contemporary Bahrain Iran map.
Understanding the Map: Tools and Projections
To fully appreciate the geopolitical nuances presented by the Bahrain Iran map, it's helpful to understand how such maps are constructed and what they represent. The map on this page, for instance, was created by the CIA in April 2019. It was produced using a Lambert Conformal Conic projection with standard parallels at 12 degrees North and 38 degrees North, and the scale of the map is 1:21,000,000. These technical details are important because they determine how accurately distances, areas, and shapes are represented, which can influence one's perception of geographical relationships.
Such maps are not just geographical tools but also political instruments, illustrating spheres of influence, potential conflict zones, and strategic locations. They serve as visual aids for understanding the intricate network of countries in the Persian Gulf or Arabian Gulf and the surrounding area, including Saudi Arabia, which is located on the Arabian Peninsula and comprises around 80% of it. Saudi Arabia's extensive borders, bound by the Red Sea to the west, Egypt and Jordan to the northeast, Iraq and Kuwait to the north, the Persian Gulf, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east, Oman to the southeast and south, as well as Yemen to the south and southwest, highlight its central role in the regional balance of power, which in turn impacts the dynamics between Bahrain and Iran.
Travel Advisories and Regional Caution
The persistent geopolitical tensions and the potential for conflict in the Middle East have tangible implications for individuals, particularly travelers. State Department travel warnings for the Middle East frequently advise Americans to steer clear of many of the region's countries or to show extra caution, with Iran and Israel often highlighted as areas of particular concern. This reflects the reality that the region, despite its rich history and culture, remains volatile.
The warnings are not merely theoretical; they are a direct consequence of the ongoing conflicts and the risk of escalation. For instance, the warning that conflict is expected to continue for several weeks, or the specific alert about a conflict zone over international waters in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea, directly impacts safety considerations for those traveling through or residing in the vicinity of the Bahrain Iran map. Understanding these advisories is crucial for anyone considering travel to the region, underscoring the real-world impact of the geopolitical landscape.
Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Geopolitical Landscape
The Bahrain Iran map is far more than a simple geographical depiction; it is a complex diagram illustrating centuries of shared history, deep-seated cultural connections, and, increasingly, profound geopolitical divergences. From Iran's historical claims and periods of domination to the strained bilateral relations post-1979 revolution, the narrative between these two nations is one of enduring tension and strategic importance.
The proximity, highlighted by the mere 768 kilometers separating them, means that any escalation in regional conflicts, particularly those involving Iran and its adversaries like Israel or the United States, directly impacts Bahrain. The presence of US military bases, the critical maritime routes in the Persian Gulf, and the constant threat of spillover from wider conflicts all contribute to a highly volatile environment. Understanding the Bahrain Iran map is therefore essential for comprehending the delicate balance of power in the Middle East and the potential for regional instability. As events continue to unfold, the world will watch closely how this critical relationship evolves. We invite you to share your thoughts on the intricate dynamics between Bahrain and Iran in the comments below, or explore our other articles on Middle Eastern geopolitics for further insights.

5 Best Places To Visit In Bahrain - Wowtovisit
Bahrain Map - Guide of the World

Why Bahrain Should Be Your Next Family Holiday