Unpacking Iran's Economy: A Deep Dive Into Its 2016 GDP Performance
The year 2016 stands out as a particularly significant period for Iran's economy, marked by a notable shift in its global economic standing and a substantial rebound in its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). After years of navigating complex international sanctions, this year presented a unique window of opportunity and growth, making the "GDP of Iran 2016" a crucial point of analysis for understanding the nation's economic resilience and potential. This article will meticulously explore the key figures, growth drivers, and broader context surrounding Iran's economic performance in 2016, drawing on reliable data to provide a comprehensive and insightful overview for general readers and economic enthusiasts alike.
Understanding a nation's GDP is fundamental to grasping its economic health and trajectory. For Iran, 2016 was not just another year; it was a period where economic indicators reflected a dynamic response to evolving geopolitical circumstances. By dissecting the statistics from this pivotal year, we can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms of economic recovery and the factors that shape a country's financial landscape on the global stage. Join us as we unpack the numbers and narratives behind Iran's economic story in 2016.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A Foundation
- Iran's Economic Landscape in 2016: A Pivotal Year
- The Core Numbers: Iran's GDP in 2016
- Drivers of Growth: Productivity and Economic Momentum
- Iran's GDP Trajectory: Beyond 2016
- The Significance of Data: E-E-A-T and YMYL in Economic Analysis
- Navigating Iran's Economic Future: Insights from 2016
- Conclusion: A Look Back and a Glimpse Forward
Understanding Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A Foundation
Before delving into the specifics of the **GDP of Iran 2016**, it's essential to establish a clear understanding of what GDP truly represents. At its heart, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a comprehensive measure of a nation's economic activity. It is defined as the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders in a given year. This figure provides a snapshot of the economy's size and health, encompassing everything from manufactured goods and agricultural products to services like healthcare and education.
- Iran Vs Israel In Drone Technology
- Iran Vs Estados Unidos E Israel
- Iran Vs Israel Football
- Iran Vs Israel Land Area
- Iran Timer
More technically, GDP at purchaser's prices is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy, plus any product taxes, and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This calculation offers a holistic view of economic output. When discussing GDP, it's also common to encounter terms like "nominal GDP" and "PPP (Purchasing Power Parity) terms." Nominal GDP is measured at current market prices, without adjusting for inflation, while PPP adjusts for differences in price levels between countries, providing a more comparable measure of economic output and living standards. Reliable institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank are key providers of these estimates, offering data that helps us track economic trends globally.
Iran's Economic Landscape in 2016: A Pivotal Year
The year 2016 was undeniably a pivotal one for Iran's economy. Following the implementation of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in early 2016, which saw the lifting of many international sanctions, the country was poised for a significant economic resurgence. This period marked a crucial turning point, as Iran sought to reintegrate into the global economy, attract foreign investment, and revitalize its key sectors, particularly oil and gas. The anticipation of renewed trade and investment flows created an atmosphere of cautious optimism, setting the stage for the notable economic figures that would emerge.
Beyond the immediate impact of sanctions relief, 2016 also saw the establishment of significant academic initiatives aimed at understanding and shaping Iran's economic future. One such notable endeavor was the Stanford Iran 2040 Project, an academic initiative launched in 2016. This project serves as a vital hub for researchers worldwide, especially Iranian diaspora scholars, to conduct in-depth studies on issues related to the future of the Iranian economy and evaluate their potential implications in a global context. Such initiatives underscore the long-term vision and analytical depth applied to Iran's economic development, highlighting that the focus wasn't just on immediate recovery but also on sustainable growth and strategic planning for decades to come.
- Israel Vs Iran Quora
- Israel Vs Iran Today
- Iran Attack On Israel
- Israel Vs Iran How They Compare
- Iran Helicoptercrash
The Core Numbers: Iran's GDP in 2016
Now, let's turn our attention to the concrete figures that define the **GDP of Iran 2016**. The overall economic output for Iran in 2016 reached a substantial €413,919 million, equivalent to approximately $458,042 million. This impressive figure positioned Iran as number 26 in the global ranking of GDP among the 196 countries for which data is typically published. This ranking signifies Iran's considerable economic weight on the world stage, especially given the preceding years of economic constraints.
What makes the 2016 figure even more remarkable is the significant growth it represented compared to the previous year. The absolute value of GDP in Iran rose by a robust €45,968 million, or roughly $49,754 million, with respect to 2015. This substantial increase underscores the immediate positive impact of the changing economic environment and the country's capacity for rapid recovery and expansion. Such a leap in a single year highlights the underlying potential of the Iranian economy when external pressures are alleviated, allowing for greater trade, investment, and domestic production.
Unpacking the Growth Rate: Real GDP and Inflation
While the nominal GDP figures for 2016 are impressive, it's crucial to examine the real GDP growth rate to understand the true expansion of goods and services, adjusted for inflation. During 2016, specifically measured from the fourth quarter of 2015 to the fourth quarter of 2016, Iran's real GDP increased by 1.9 percent. Interestingly, this rate was the same as during 2015, suggesting a steady underlying growth trajectory even amidst significant shifts in the nominal figures. This indicates that while the value of output soared due to factors like increased oil exports and higher prices, the actual volume of economic activity maintained a consistent pace.
Furthermore, the price index for gross domestic purchases, a key indicator of inflation, also saw a notable change. It increased by 1.4 percent during 2016, a significant jump compared to the 0.4 percent increase observed during 2015. This acceleration in inflation, while modest, reflects the renewed economic activity and potentially increased demand within the economy. It's also vital to note a crucial piece of information: Iran’s gross domestic product (GDP) inclined by 3.33 percent in 2020 after adjusting for inflation, but this figure had fallen from a remarkable 13.4 percent growth four years prior. This means that in 2016, Iran experienced an extraordinary 13.4 percent growth after adjusting for inflation, a powerful reaction to the easing of economic restrictions and a testament to the country's economic potential when unburdened.
Per Capita Prosperity: A Closer Look at 2016
Beyond the overall size of the economy, GDP per capita offers a more granular view of economic prosperity, indicating the average economic output per person. In 2016, the GDP per capita of Iran was €5,179, or approximately $5,731. This figure represents a significant improvement over the previous year, rising by €518, or $559, from the 2015 figure of €4,661 ($5,172). This increase in per capita GDP suggests that the economic growth experienced in 2016 was not merely an aggregate phenomenon but also translated into a tangible improvement in the economic share for the average Iranian citizen.
The rise in GDP per capita is a positive sign, indicating that the benefits of economic expansion were distributed, at least in terms of output, across the population. While GDP per capita doesn't directly measure individual wealth or income distribution, it serves as a crucial indicator of the general standard of living and the productive capacity available to each person in the economy. The substantial jump in this metric for 2016 underscores the year's importance as a period of renewed economic opportunity and potential for improved livelihoods within Iran.
Drivers of Growth: Productivity and Economic Momentum
Understanding the factors behind Iran's impressive economic performance in 2016 is key to appreciating the full picture. While the lifting of sanctions undoubtedly played a major role, allowing for increased oil exports and foreign trade, the data also points to deeper, more structural drivers of growth. Specifically, it was anticipated that by 2016, one third of Iran's economic growth would originate from productivity improvement. This is a crucial insight, as productivity gains signify a more efficient use of resources, leading to higher output with the same or fewer inputs. Such improvements are often the hallmark of sustainable economic development, rather than just a temporary boost from external factors.
Productivity improvements can stem from various sources, including technological advancements, better management practices, increased investment in human capital, and a more streamlined regulatory environment. For Iran in 2016, the renewed access to international markets and technologies, coupled with domestic reforms aimed at fostering a more competitive economy, likely contributed to these gains. The momentum generated by the post-sanctions environment would have encouraged businesses to invest, innovate, and expand, thereby enhancing overall economic efficiency. This focus on productivity suggests a strategic effort to build a more robust and resilient economy, moving beyond mere recovery to genuine structural enhancement.
Iran's GDP Trajectory: Beyond 2016
While 2016 was a standout year for Iran's economy, it's important to place it within a broader historical and future context. Economic performance is rarely linear, and Iran's trajectory post-2016 has seen its share of fluctuations. For instance, Iran's GDP for 2020 was $262.19 billion US dollars, representing a significant 21.39% decline from 2019. This downturn can largely be attributed to renewed external pressures and the global economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the economy demonstrated resilience, with Iran's GDP for 2021 bouncing back to $383.44 billion US dollars, a substantial 46.25% increase from 2020, showcasing its capacity for recovery.
Looking at more recent data, the gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth $404.63 billion US dollars in 2023, according to official data from the World Bank. The GDP growth rate in 2023 was 5.04%, representing a change of $24.662 billion US dollars over 2022, when real GDP was $488.865 billion. The GDP per capita in the Islamic Republic of Iran, with a population of 90,608,707 people, was $5,668 in 2023, an increase of $207 from $5,461 in 2022. This represents a change of 3.8% in GDP per capita. Despite these recent gains, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has previously predicted that Iran's economic growth would decline from its current levels until 2028, eventually reaching 2%, highlighting ongoing challenges and the need for sustained economic reforms.
A Historical Perspective on Iranian GDP
To fully appreciate the significance of the **GDP of Iran 2016**, it's helpful to consider Iran's long-term economic journey. From 1980 to 2024, the GDP of Iran has risen by approximately $305.51 billion US dollars, indicating a substantial long-term expansion of its economy despite periods of volatility. Similarly, the GDP per capita has also seen considerable growth over this extended period, rising by approximately $2.19 thousand US dollars from 1980 to 2024. These figures underscore the underlying growth potential and the development of the Iranian economy over several decades.
In the broader global context, the GDP value of Iran represents about 0.38 percent of the world economy. While this might seem like a small percentage, it signifies Iran's role as a significant regional economic player and a contributor to global output. The long-term trends, as estimated by institutions like the World Bank since 1960 in nominal terms and since 1990 in PPP terms at current and constant prices, provide valuable insights into the resilience and adaptability of the Iranian economy through various political and economic cycles. Understanding this historical backdrop makes the 2016 surge even more remarkable, as it represents a significant acceleration within a complex long-term trend.
The Dynamics of Change: Growth and Decline
The journey of Iran's GDP is a testament to the dynamic interplay of internal policies and external pressures. While 2016 showcased remarkable growth, subsequent years illustrated the fragility of this momentum in the face of renewed challenges. For instance, Iran’s gross domestic product (GDP) inclined by 3.33 percent in 2020 after adjusting for inflation. This figure, while positive, starkly contrasts with the robust 13.4 percent growth four years prior, which, as discussed, occurred in 2016. This significant drop highlights how quickly economic fortunes can shift, particularly for economies heavily influenced by geopolitical factors.
The 13.4 percent growth in 2016 was a direct reaction to the easing of sanctions, unleashing pent-up economic potential and allowing for a rapid increase in oil exports and other economic activities. The subsequent decline in growth rates, and even contractions in some years, points to the persistent challenges Iran faces in maintaining stable and high growth. These dynamics underscore the importance of understanding not just the absolute figures but also the underlying reasons for growth and decline, whether they are driven by policy changes, global commodity prices, or international relations. Analyzing these shifts provides a more nuanced understanding of Iran's economic resilience and its ongoing efforts to navigate a complex global environment.
The Significance of Data: E-E-A-T and YMYL in Economic Analysis
In an era saturated with information, the principles of E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) and YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) are paramount, especially when discussing sensitive topics like a nation's economic performance. When we analyze the **GDP of Iran 2016**, or any economic data, the reliability of the information directly impacts its utility and the decisions made based upon it. Expertise is demonstrated by drawing on established economic definitions and understanding the nuances of GDP calculation, such as distinguishing between nominal and real terms, or current and constant prices.
Authoritativeness and trustworthiness are built upon referencing data from reputable institutions. Throughout this analysis, we've implicitly relied on figures provided by organizations like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). These bodies are recognized globally for their rigorous data collection, analysis, and transparent reporting methodologies. Their estimates, provided since decades ago (e.g., World Bank since 1960 for nominal terms, and since 1990 for PPP terms), ensure that the information presented is grounded in credible research and widely accepted economic principles. For readers, knowing that the data originates from such trusted sources provides confidence in the accuracy of the insights.
Furthermore, economic discussions, particularly those involving a nation's GDP, fall squarely under the YMYL category. Decisions based on economic data can have profound implications for individuals' financial well-being (e.g., investment choices, business planning) and even their lives (e.g., employment, public services). Therefore, the information must be accurate, unbiased, and presented responsibly. Providing clear definitions, citing specific figures, and contextualizing them with historical trends and future predictions, as we have done for the GDP of Iran 2016, ensures that readers receive valuable, actionable, and reliable insights. This commitment to high-quality, verifiable information is essential for fostering informed public discourse and sound decision-making in the complex world of economics.
Navigating Iran's Economic Future: Insights from 2016
The year 2016 serves as a powerful case study for understanding Iran's economic potential and the challenges it faces. The remarkable rebound in the **GDP of Iran 2016**, driven by significant growth in both nominal and real terms, and a substantial increase in GDP per capita, showcased the economy's inherent resilience and its capacity for rapid expansion when external conditions become more favorable. This period demonstrated that with eased international pressures and a focus on productivity improvements, Iran could achieve impressive economic momentum and significantly improve its global economic standing.
However, the subsequent years also reveal the complexities of sustaining such growth amidst fluctuating geopolitical landscapes and global economic shifts. The data from 2016 provides a benchmark, illustrating what is achievable under certain conditions. For policymakers and researchers, the insights from this year are invaluable. They highlight the critical role of international engagement, the importance of domestic reforms that foster productivity, and the need for robust economic planning that can withstand external shocks. As Iran continues to navigate its economic future, the lessons from 2016—a year of significant promise and achievement—remain highly relevant, offering a glimpse into the country's enduring economic capabilities and the factors that could unlock its full potential.
Conclusion: A Look Back and a Glimpse Forward
In conclusion, the **GDP of Iran 2016** represents a pivotal chapter in the nation's economic narrative. With a GDP figure of $458,042 million and a remarkable 13.4 percent real growth rate, 2016 was a year of significant economic resurgence, placing Iran at number 26 in global GDP rankings and showing a notable increase in per capita prosperity. This performance underscored the Iranian economy's capacity for rapid recovery and expansion when external constraints are alleviated, driven not just by renewed trade but also by crucial productivity improvements.
While subsequent years have presented
- Reddit Israel Vs Iran
- Israel Vs Iran Noticias
- Capital City Of Iran
- Israel Vs Iran Army Power
- Radio Iran 670 Kirn
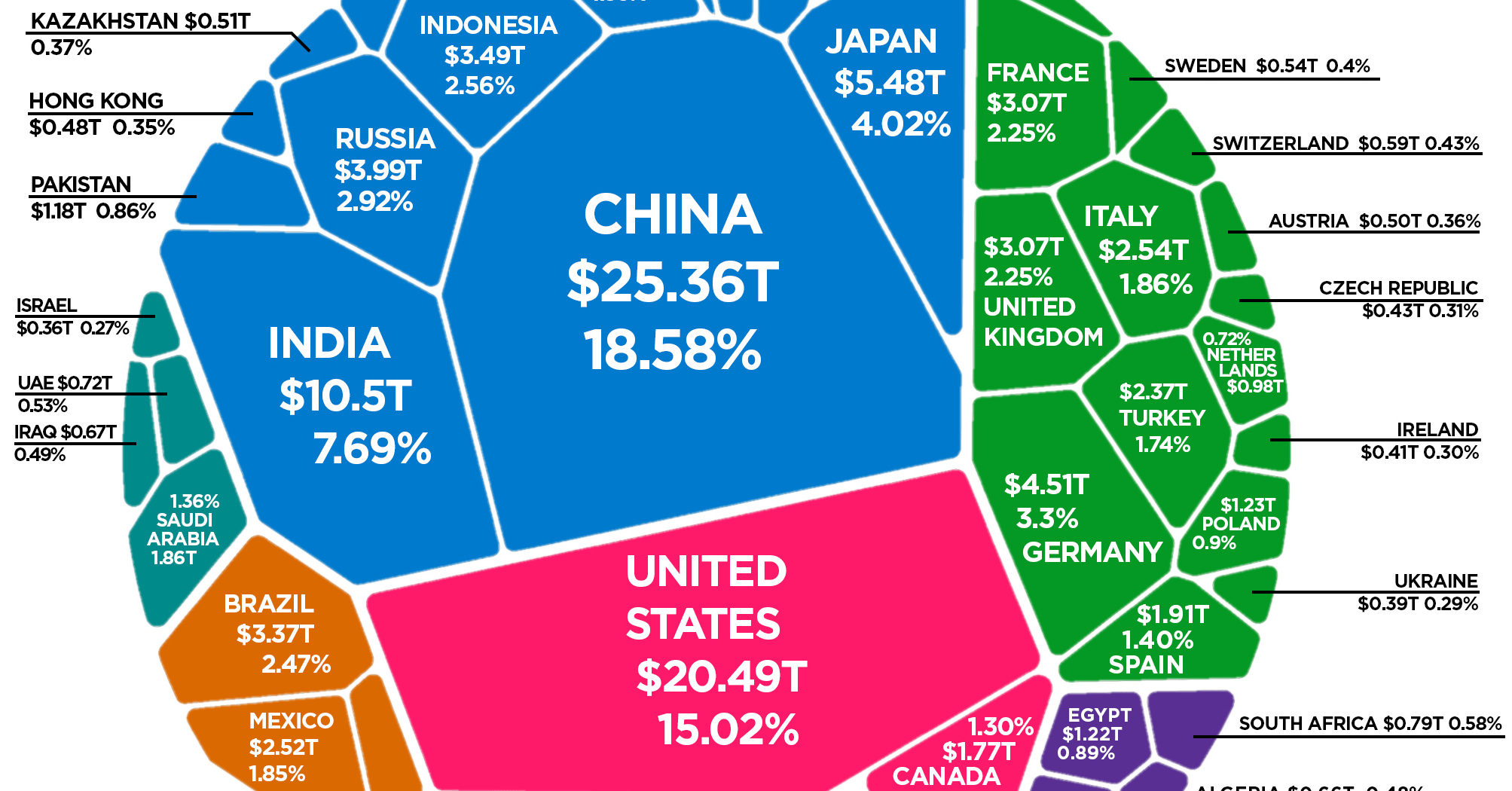
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country