Unveiling The Baloch Population In Iran: A Deep Dive
Table of Contents
- Who Are the Baloch People?
- The Baloch Presence in Iran: Numbers and Distribution
- Beyond Iran's Borders: A Transnational Community
- Cultural Identity and Societal Fabric
- Challenges and Human Rights Concerns
- Economic Landscape and Social Mobility
- The Future of the Baloch Community in Iran
Who Are the Baloch People?
The Baloch are an ancient ethnic group with a distinct cultural identity, primarily inhabiting the Balochistan region, a vast and often challenging geographical area that spans parts of Pakistan, Iran, and Afghanistan. Their history is one of resilience, adaptation, and a strong sense of communal identity forged over centuries. The term "Baloch" itself refers to a group of tribes speaking the Balochi language, a testament to their shared linguistic heritage. This linguistic and cultural community has developed independently over time, with its largest concentration found in Pakistan, followed by Iran, Afghanistan, Oman, Bahrain, and Turkmenistan. Their name, Baluch/Baloch, is steeped in historical and cultural significance, though its precise etymology remains a subject of some academic discussion.Origins and Identity
The origins of the Baloch are debated among historians, with theories tracing them back to ancient Arabian tribes, Central Asian nomads, or even early Iranian peoples. Regardless of their precise historical genesis, the Baloch have established themselves as a unique ethnic group, characterized by their tribal structures, a strong code of honor (known as "Baloch Mayar"), and a deep connection to their ancestral lands. Over the course of history, the Baloch developed into an independent linguistic and cultural community, maintaining their traditions despite living across multiple national borders. Their identity is further shaped by their predominantly Sunni Muslim faith, which often distinguishes them from the Shi'a majority in Iran.Linguistic Diversity
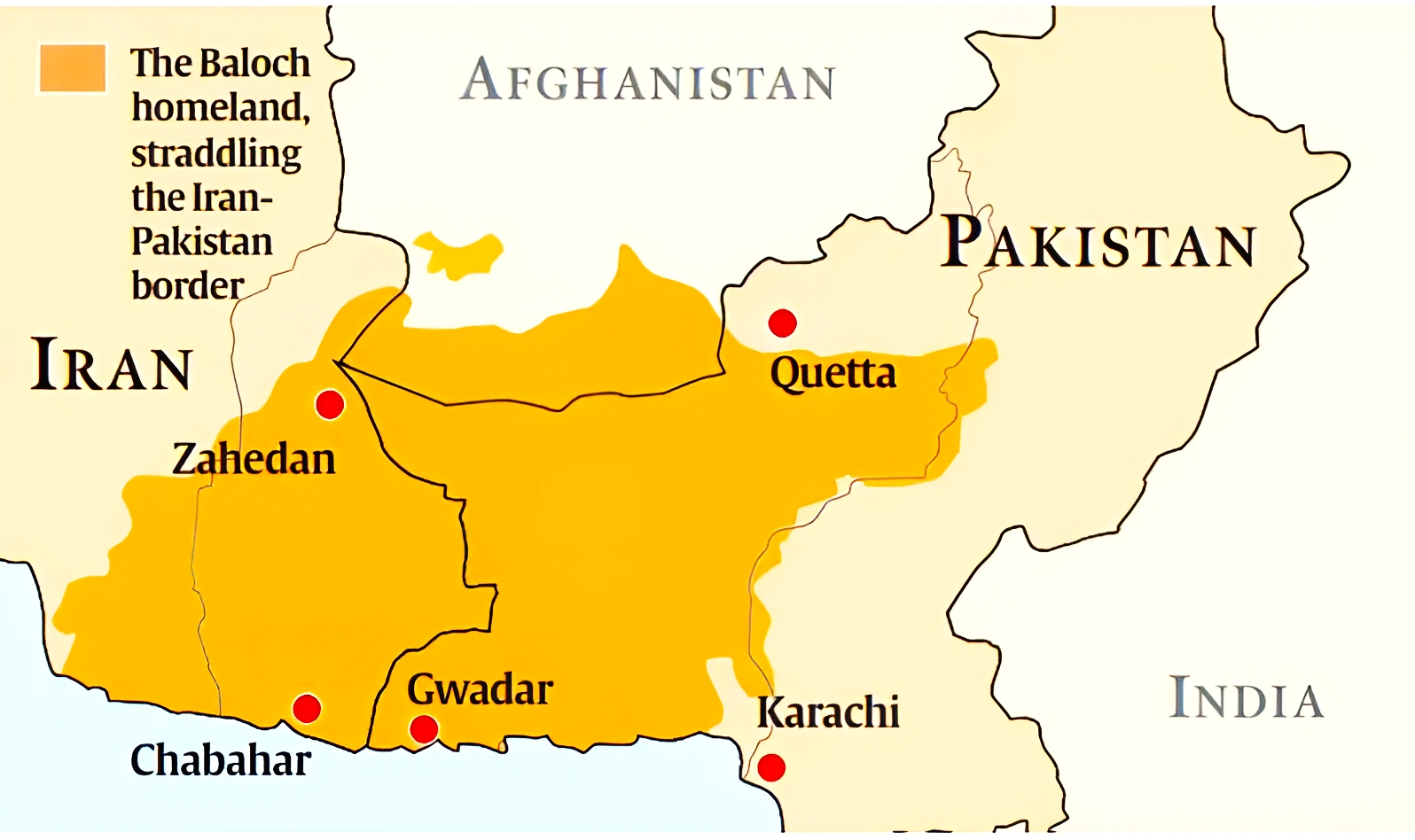
Language is a cornerstone of Baloch identity. Most Baloch speak one of the three main dialects of the Balochi language: Eastern Balochi, Southern Balochi, or Western Balochi. This linguistic diversity reflects the wide geographical spread of the Baloch people and the historical interactions between different tribal groups. While these dialects share a common root, they possess distinct phonetic and lexical variations. The Western Balochi dialect is particularly relevant to the Baloch population in Iran, as their homeland straddles the borders of Iran and Pakistan. Despite the challenges of maintaining linguistic heritage in diverse national contexts, the Balochi language remains a vital component of their cultural preservation and a key marker of their ethnic identity.The Baloch Presence in Iran: Numbers and Distribution
Understanding the precise number of the Baloch population in Iran is a complex task, as reliable, official statistics are often scarce or not publicly disaggregated by ethnicity. However, various estimates and demographic analyses provide insights into their significant presence within the country. The Baloch are not merely a minority; they constitute a substantial portion of the population in specific regions, making them a crucial demographic group to consider when discussing Iran's overall social and political landscape.Estimating the Population
Estimates of the Iranian Baloch population vary, ranging from 2.5 to 4 million [8] [2]. Other sources suggest that in Iran there are about two million ethnic Baloch [50]. These figures highlight the challenge in obtaining definitive numbers, but they consistently point to a significant community. While there are no reliable statistics regarding the total number of Baloch people globally, in 2013, their population was estimated at around 10 million across all regions where they reside. The combined population of Baloch people in the five provinces where they are most concentrated in the broader region is over 4.8 million, which accounts for 5.51% of Iran’s total population of 87 million. This indicates that while they are a minority nationally, their regional concentration is considerable. It's also noted that even though they only make up about 2% of the Iranian population, they account for a disproportionately high number of executions, a concerning statistic that will be explored further.Geographic Concentration
The largest concentration of the Baloch population in Iran is found in the eastern Sistan and Baluchestan province, where a majority of the population is of Baloch ethnicity. This province serves as the historical heartland of the Baloch in Iran, characterized by its unique cultural landscape and the strong presence of Baloch traditions. However, the Baloch population is not confined to this single province. Smaller communities of Kurds (in the eastern highlands and near Iranshahr), the expatriate Brahui (along the border with Pakistan), and other resident and itinerant ethnic groups, such as the Romani, are also found within the province, contributing to its diverse demographic makeup. While Sistan and Baluchestan is their primary stronghold, the Baloch are also scattered across other parts of Iran, reflecting historical migrations and economic opportunities.Beyond Iran's Borders: A Transnational Community
The Baloch are a truly transnational community, with their historical homeland straddling the borders of Iran, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. This geographical spread has shaped their identity, culture, and socio-political experiences, creating a shared heritage that transcends national boundaries. The largest portion of the Baloch population, both in terms of area and numbers, resides outside Iran, particularly in Pakistan.Baloch in Pakistan
The largest concentration of Baloch people is in Pakistan. Pakistan's largest province by land area is Balochistan, and it is here that about 50% of the total Baloch population lives. An estimated 6.9 million of Pakistan's population is Baloch. Furthermore, a significant, albeit smaller, number of Baloch reside in Pakistan's Sindh province (accounting for 40% of the total Baloch population) and the Pakistani Punjab. This dominant presence in Pakistan means that the experiences of the Baloch in Iran are often viewed in the broader context of the Baloch nationalist movements and socio-economic conditions in Pakistan. The western Baloch, in particular, are part of a much larger population of several million, with a majority living in Pakistan, highlighting the deep cross-border connections.Baloch in Afghanistan and Other Regions
Beyond Pakistan, Baloch people also reside in 24 provinces across Afghanistan, including Nimroz, Farah, Helmand, Kandahar, and Herat. Their presence in Afghanistan, while smaller than in Pakistan or Iran, is historically significant, reflecting ancient trade routes and tribal movements. Furthermore, increasing numbers of Baloch are migrating to Oman and the United Arab Emirates, forming expatriate communities. Regions with significant populations also include Oman (estimated 80,000 [2]), UAE (estimated 46,800 [1]), India (estimated 1,000 [2]), and Turkmenistan. This global dispersion underscores the resilience and adaptability of the Baloch people, who have maintained their cultural identity across diverse national contexts.Cultural Identity and Societal Fabric
The cultural identity of the Baloch population in Iran is deeply intertwined with their language, tribal customs, and religious practices. As a predominantly Sunni Muslim community in a Shi'a-majority nation, their religious identity plays a significant role in shaping their societal fabric and interactions with the broader Iranian state. Their cultural practices, including traditional dress, music, and oral literature, are distinct and have been preserved through generations, often serving as a source of pride and communal cohesion. The tribal structure remains an important aspect of Baloch society, even in modern contexts, influencing social hierarchies, dispute resolution, and community solidarity. This traditional framework, combined with their unique language and customs, sets them apart from the Persian majority and other ethnic groups in Iran. Despite facing various challenges, the Baloch have maintained a vibrant cultural life, contributing to the rich diversity of Iranian society. However, this distinctiveness can also lead to issues of recognition and integration within the national framework.Challenges and Human Rights Concerns
The Baloch population in Iran faces a unique set of challenges, many of which stem from their status as an ethnic and religious minority. These challenges often manifest as human rights issues, impacting their daily lives, access to opportunities, and fundamental freedoms. The sensitivity of these issues makes it crucial to examine them through the lens of human rights, which are universal and inalienable.Discrimination and Marginalization
According to several international reports, Balochis have faced government discrimination, both as Sunni religious practitioners and as an ethnic minority group. This discrimination often translates into limited opportunities and systemic marginalization. For instance, the data suggests that only a few Baloch individuals enjoy senior positions in government. This has resulted mainly from unfair treatment in public employment or discrimination between the Sunni Baloch. Such disparities in public employment and other sectors can lead to economic hardship and a sense of disenfranchisement among the Baloch community, exacerbating existing socio-economic vulnerabilities.Religious Freedom and Identity Cards
Religious freedom is another significant concern for the Baloch population in Iran. As Sunni Muslims, they often face restrictions on their religious activities. According to Baloch activists, the Iranian state controls and imposes many restrictions on their religious activities. A particularly distressing consequence of these restrictions is the refusal of national identity cards for their children. Without identity cards, individuals face immense difficulties in accessing basic services like education, healthcare, and formal employment, effectively rendering them stateless within their own country. This issue highlights a profound human rights violation that directly impacts the future generations of the Baloch community. Many Baloch people are harassed or beaten, further illustrating the pressures they endure.Executions and Targeted Actions
Perhaps one of the most alarming human rights issues impacting Iran's Baloch population is the disproportionately high number of executions they face. As Dudoignon notes, "the Baloch population is used to being targeted for a high number of executions." This is particularly stark when considering that "even though they only make up 2% of the Iranian population they account for more than a [disproportionate number of] executions." This statistic raises serious concerns about due process, fair trials, and the potential for ethnic and religious targeting within the justice system. The high rate of executions contributes to a climate of fear and insecurity within the Baloch community, underscoring the severe human rights challenges they navigate.Economic Landscape and Social Mobility
The economic landscape of Sistan and Baluchestan province, where the majority of the Baloch population in Iran resides, is often characterized by underdevelopment and limited opportunities compared to other regions of Iran. While Iran's nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is $418 billion, ranking it 36th globally, this national wealth does not always translate into equitable development across all provinces or benefit all ethnic groups. The Baloch regions frequently suffer from high unemployment rates, inadequate infrastructure, and limited access to quality education and healthcare services. The marginalization in public employment, as mentioned earlier, further constrains social mobility for the Baloch. This can lead to a cycle of poverty and limited prospects, prompting some to seek opportunities elsewhere, including migration to other Iranian cities or even to countries like Oman and the UAE. While the Baloch are known for their entrepreneurial spirit, especially in cross-border trade, formal economic integration and opportunities for advancement within the national economy remain significant challenges. Addressing these economic disparities is crucial for improving the living standards and fostering greater social cohesion for the Baloch population in Iran.The Future of the Baloch Community in Iran
The future of the Baloch population in Iran is intrinsically linked to broader national policies concerning ethnic and religious minorities, as well as regional stability. Their resilience, cultural vibrancy, and strong communal ties suggest a continued presence and assertion of their identity. However, the persistent challenges related to human rights, discrimination, and economic marginalization pose significant hurdles. For the Baloch community, the path forward involves a delicate balance between preserving their unique cultural and religious identity and advocating for greater inclusion and equitable treatment within the Iranian state. Increased recognition of their rights, fair representation in governance, and targeted development initiatives in their regions could foster greater integration and prosperity. The international community's attention to the human rights situation of the Baloch can also play a role in advocating for positive change and accountability. Ultimately, the future well-being of the Baloch population in Iran hinges on the state's willingness to embrace its diverse population and ensure that all its citizens, regardless of ethnicity or religion, enjoy equal rights and opportunities.Conclusion
The Baloch population in Iran is a vital and integral part of the country's rich tapestry, contributing significantly to its cultural and historical landscape. While their exact numbers vary in estimates, ranging from 2.5 to 4 million, their concentration in the Sistan and Baluchestan province is undeniable, making them a key demographic force in the region. Their transnational identity, with strong ties to communities in Pakistan and Afghanistan, further underscores their unique position. Despite their deep roots and cultural resilience, the Baloch community in Iran faces profound challenges, including systemic discrimination, restrictions on religious freedom, and disproportionately high rates of executions. These issues highlight a critical need for greater attention to their human rights and socio-economic development. Understanding the complexities faced by the Baloch is not merely an academic exercise; it is essential for promoting human rights, fostering social justice, and building a more inclusive society. We encourage you to delve deeper into the experiences of minority groups worldwide and consider how diverse populations contribute to the global human story. What are your thoughts on the challenges faced by ethnic minorities in different parts of the world? Share your insights in the comments below, and consider exploring other articles on our site that shed light on diverse communities and human rights issues.- Israel Vs Iran On Map
- Israel Attack Iran Wikipedia
- Helicoptercrash Iran
- How Strong Is Iran Military Vs Israel
- Iran Vs Israel And Saudi Arabia

Baloch Girl Child Iran - Free photo on Pixabay
Iran Pakistan Relations And The Baloch Militancy - PWOnlyIAS

Baloch people - BORGEN